Here’s a detailed 1000-word blog for “The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Fertilizer for Your Crops”:
The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Fertilizer for Your Crops
Agriculture is the backbone of any economy, and successful crop production hinges on one critical factor: soil fertility. While nature provides many of the nutrients crops need, modern farming often demands more. Fertilizers play an indispensable role in ensuring crops get the nutrients they require to thrive. But with countless options available, how do you select the right fertilizer for your needs? This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know to make the best choice.
Understanding Fertilizers: What Are They
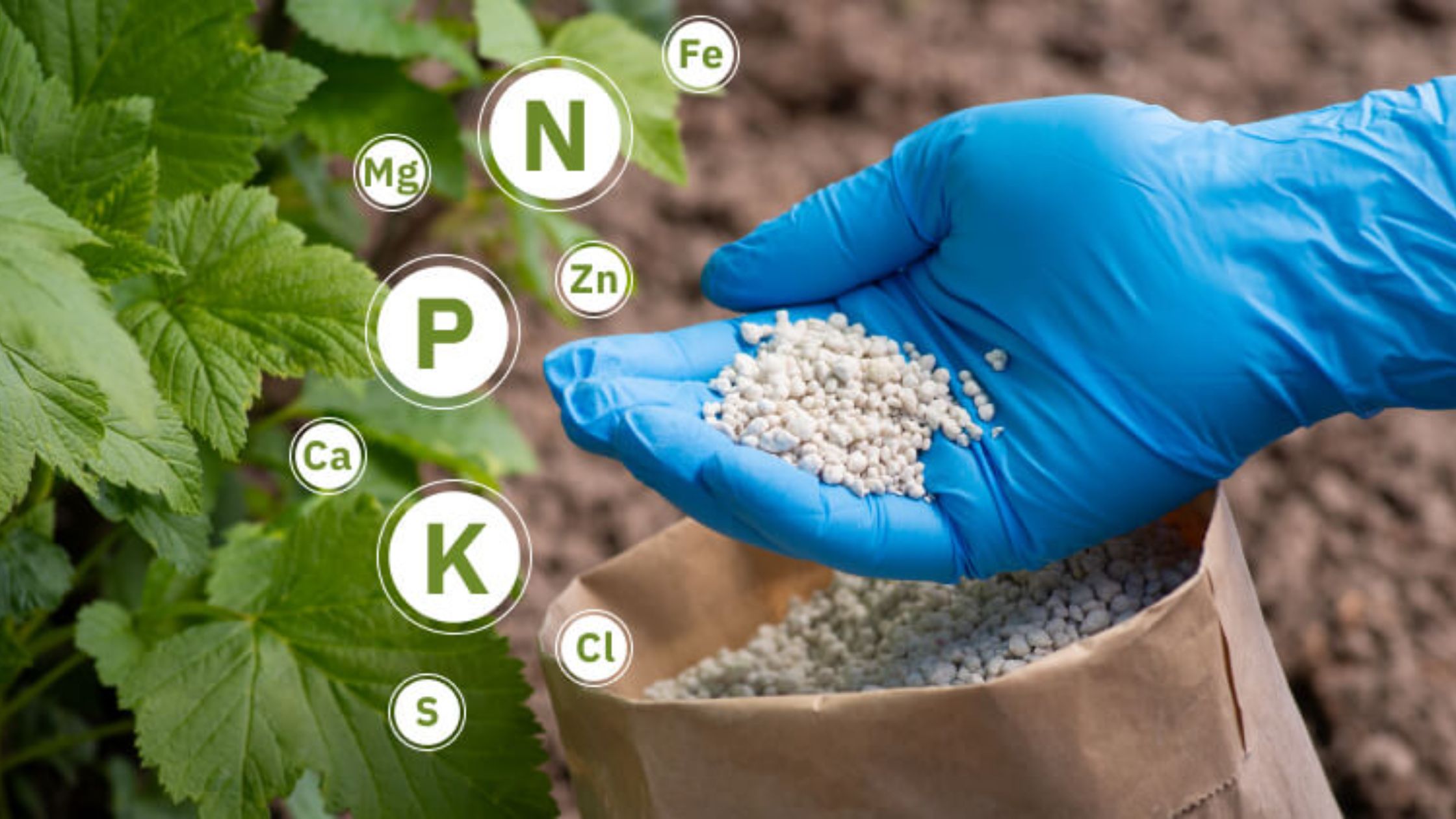
Fertilizers are substances that provide essential nutrients to plants. These nutrients are divided into three categories:
- Macronutrients (Primary Nutrients): Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K) are the most crucial for plant growth and are often the main ingredients in fertilizers.
- Secondary Nutrients: Calcium (Ca), Magnesium (Mg), and Sulfur (S) are equally important but required in smaller amounts.
- Micronutrients: Elements like Zinc (Zn), Iron (Fe), Manganese (Mn), and Boron (B) are needed in trace amounts but are vital for healthy plant development.
Each crop and soil type has unique requirements, which makes choosing the right fertilizer a science as much as an art.
Why Is Choosing the Right Fertilizer Important?
Using the wrong fertilizer can have severe consequences:
- Under-fertilization: Leads to stunted growth, low yields, and poor-quality produce.
- Over-fertilization: Causes nutrient runoff, soil degradation, and harm to the environment, including water pollution.
Proper fertilizer selection ensures:
- Optimal plant growth and maximum yield.
- Cost-effectiveness, as you’re not wasting money on unnecessary nutrients.
- Environmental sustainability by reducing wastage and minimizing harmful runoff.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Fertilizers
- Soil Testing
The first step in selecting the right fertilizer is understanding your soil’s nutrient profile. Soil testing provides a detailed report of nutrient levels, pH, and organic matter content. Based on this, you can determine which nutrients are deficient and need supplementation. - Crop Requirements
Different crops have different nutrient needs. For instance:
- Corn requires high nitrogen levels during its growth phase.
- Legumes like peas and beans need less nitrogen since they can fix it from the atmosphere.
- Fruits and flowers often require fertilizers rich in potassium for better color, flavor, and storage life.
- Type of Fertilizer
Fertilizers come in various forms:
- Chemical (Synthetic) Fertilizers: Fast-acting and nutrient-specific but can lead to soil degradation if overused.
- Organic Fertilizers: Derived from natural sources like compost or animal manure. They improve soil health but act slowly.
- Bio-fertilizers: Contain live microorganisms that enhance nutrient availability in the soil.
- Slow-release Fertilizers: Release nutrients over an extended period, ensuring steady plant growth.
- Application Method
Some fertilizers are best suited for specific application methods:
- Broadcasting: Spreading fertilizer evenly across the field.
- Foliar Feeding: Spraying liquid fertilizer directly on plant leaves for quick absorption.
- Drip Fertigation: Applying fertilizer through an irrigation system for targeted delivery.
- Weather and Timing
Weather conditions and the growth stage of the crop play a significant role:
- Fertilize just before rainfall to help nutrients seep into the soil.
- Avoid application during extremely hot or cold weather, as it reduces nutrient absorption.
Understanding Fertilizer Labels
Fertilizer bags often display three numbers, such as 10-20-10. These indicate the percentage of primary nutrients in the fertilizer:
- Nitrogen (N): Promotes leafy growth.
- Phosphorus (P): Enhances root development and flowering.
- Potassium (K): Improves plant resistance to diseases and drought.
For example, a 10-20-10 fertilizer contains:
- 10% Nitrogen.
- 20% Phosphorus.
- 10% Potassium.
Choose the ratio that best suits your crop and soil needs.
Balancing Cost and Effectiveness
Fertilizers can be expensive, especially specialty types. Balancing cost and effectiveness is crucial:
- Invest in quality fertilizers for high-value crops like fruits and vegetables.
- Use bulk or generic fertilizers for staple crops like wheat or rice.
- Opt for slow-release or bio-fertilizers to save costs in the long run.
Common Fertilizers and Their Uses
- Urea (46% Nitrogen): Best for nitrogen-deficient soils and promotes lush green growth.
- DAP (Diammonium Phosphate): A popular choice for phosphorus supplementation.
- Potash (Potassium Chloride): Ideal for improving crop resilience and quality.
- Compost: An all-purpose organic fertilizer that enriches soil structure.
- Liquid Fertilizers: Great for foliar feeding or fertigation.
Steps to Choose the Right Fertilizer
- Test Your Soil: Identify deficiencies and pH imbalances.
- Understand Crop Needs: Research the nutrient requirements of your specific crop.
- Match Fertilizer Composition: Look for a fertilizer that fulfills the deficient nutrients.
- Consult an Expert: Agronomists or services like AoneCrop can provide tailored advice.
- Start Small: Test the fertilizer on a small section before applying it to your entire field.
Tips for Maximizing Fertilizer Efficiency
- Apply at the Right Time: Fertilize during the crop’s active growth phase.
- Use Proper Techniques: Avoid uneven application to prevent nutrient imbalances.
- Combine with Organic Matter: Mixing chemical fertilizers with organic matter enhances their efficiency.
- Practice Crop Rotation: Rotating crops reduces the risk of nutrient depletion and ensures balanced soil fertility.
Why Choose AoneCrop for Your Fertilizer Needs?
At AoneCrop.com, we understand the unique challenges farmers face. That’s why we offer a range of high-quality fertilizer solutions tailored to your specific needs:
- Comprehensive Soil Testing Services: Get a detailed analysis of your soil’s nutrient levels.
- Custom Fertilizer Recommendations: Our experts guide you in choosing the best products.
- Eco-Friendly Options: We prioritize sustainability with our range of bio and organic fertilizers.
Conclusion
Fertilizer selection is more than just a purchase; it’s an investment in your crop’s future. By understanding your soil, crop requirements, and available options, you can make informed decisions that maximize yield and minimize environmental impact.
Ready to optimize your farming practices? Explore AoneCrop’s premium range of fertilizers today and give your crops the nutrients they deserve.
Would you like me to write the next blog, or would you like to provide input or make adjustments to this one?